.hidden-from-title { display: none !important; }
/* Show the image in the actual post content */ .post-content .hidden-from-title { display: block !important; }
GUI Execution Artifact - Program Compatibility Assistant

In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital forensics, the discovery of new artifacts is a rare and exciting event. Windows 11 version 22H2 introduced a significant new forensic artifact that has captured the attention of the DFIR (Digital Forensics and Incident Response) community: the Program Compatibility Assistant (PCA) artifact
What is the PCA Artifact?
The Program Compatibility Assistant (PCA) is not entirely new to Windows – it has existed since Windows Vista as a mechanism to detect and fix compatibility issues in legacy applications when they are executed on newer versions of Windows. However, what’s revolutionary about Windows 11 22H2 is that the PCA service (PcaSvc) now stores additional execution data in text files, creating a new source of evidence for digital forensic investigators
This artifact provides evidence of execution specifically for GUI-based programs, making it a valuable addition to the forensic analyst’s toolkit alongside traditional artifacts like Prefetch, Amcache, and ShimCache23.
Artifact Location and Structure
The PCA artifact resides in the following directory:
C:\Windows\appcompat\pca\
This location contains three key files
PcaAppLaunchDic.txtPcaGeneralDb0.txtPcaGeneralDb1.txt
PcaAppLaunchDic.txt: The Primary Artifact
The most significant file for forensic analysis is PcaAppLaunchDic.txt.This pipe-delimited text file contains a simple but powerful format:
[Full Executable Path] | [Last Execution Timestamp] For example: C:\Program Files\Everything\Everything.exe|2022-12-28 16:06:24.212 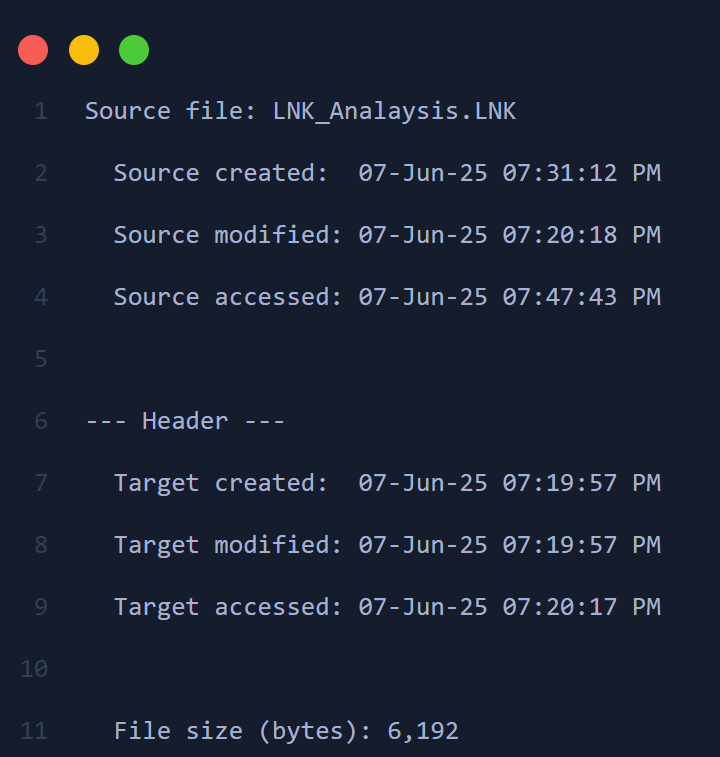
The timestamp represents the last time the specified executable was executed and is stored in UTC format. Importantly, this timestamp is recorded when the process terminates, not when it starts
PcaGeneralDb0.txt: Extended Execution Details
The PcaGeneralDb0.txt file contains more detailed information about executed programs, including:
Runtime timestamp
Run status
Full path to the binary
Description of the file
Software vendor
File version
Program ID (which can be cross-referenced with Amcache for enhanced analysis
PcaGeneralDb1.txt: Secondary Database
The PcaGeneralDb1.txt file appears to serve as a secondary database, though research indicates it may not always be populated or updated in all testing scenarios.
Forensic Value and Analysis
Evidence of Execution
The PCA artifact provides reliable evidence of program execution similar to other well-established artifacts like Prefetch and Amcache. This is particularly valuable for:
Timeline analysis of program execution
Identifying malicious software that has been run on a system
Incident response investigations where understanding program execution history is crucial
Cross-referencing with other artifacts for comprehensive analysis
Integration with Existing Artifacts
One of the most powerful aspects of the PCA artifact is its ability to be correlated with Amcache. The Program ID field in PcaGeneralDb0.txt can be matched with Amcache entries, allowing investigators to create a more complete picture of program execution and installation history.
Limitations and Considerations
While the PCA artifact is valuable, it’s important to understand its limitations:
- Windows 11 22H2 specific: This artifact only exists in Windows 11 version 22H2 and later.
- GUI programs only: It primarily tracks graphical user interface applications
- Process termination timing: Timestamps reflect when processes end, not when they begin
- Limited deployment: As Windows 11 22H2 adoption is still growing (currently at 42.66% globally), this artifact may not be present in all investigations
Practical Implementation
Tool Support
The forensic community has quickly adapted to support this new artifact:
Velociraptor has developed specific artifacts for PCA analysis6
KAPE includes targets for collecting PCA files7
Custom parsing tools have been developed by the community8
Investigation Workflow
When analyzing PCA artifacts, forensic investigators should:
Collect all three PCA files from the target system
Parse PcaAppLaunchDic.txt for basic execution evidence
Analyze PcaGeneralDb0.txt for detailed program information
Cross-reference with Amcache using Program IDs
Integrate findings into timeline analysis and case documentation
Future Implications
The discovery of the PCA artifact represents a significant advancement in Windows forensics1. As Windows 11 22H2 becomes more prevalent in enterprise environments, this artifact will become increasingly valuable for:
Incident response teams investigating security breaches
Malware analysis and threat hunting activities
Corporate investigations requiring evidence of program execution
Timeline reconstruction in complex forensic cases
Conclusion
The Windows 11 22H2 PCA artifact fills an important gap in digital forensics by providing clear, text-based evidence of GUI program execution2. Its simple format makes it easily parseable, while its integration capabilities with existing artifacts like Amcache enhance its investigative value16.
As the digital forensics community continues to research and develop tools for this artifact, it promises to become a cornerstone of Windows 11 forensic analysis9. For DFIR professionals, understanding and leveraging the PCA artifact will be essential as Windows 11 deployment continues to expand across enterprise environments.
The discovery and documentation of this artifact by researchers like Andrew Rathbun and Lucas Gonzalez, along with continued research by teams at Sygnia, demonstrates the importance of ongoing forensic research in keeping pace with evolving operating systems and their investigative potential12.
- https://www.sygnia.co/blog/new-windows-11-pca-artifact/
- https://aboutdfir.com/new-windows-11-pro-22h2-evidence-of-execution-artifact/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rV8aErDj06A
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/stephan-berger-59575a20a_im-playing-around-with-the-program-compatibility-activity-7283872364231049216-09wE
- https://www.forensic-cheatsheet.com/EN/Artifact/(EN)+PCA
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/idan-abramovich-b16a4211a_new-windows-11-pro-22h2-evidence-of-execution-activity-7320449133717155840-s6_H
- https://github.com/EricZimmerman/KapeFiles/blob/master/Targets/Windows/AppCompatPCA.tkape
- http://windowsir.blogspot.com/2023/04/program-execution.html
- https://www.techzine.eu/blogs/security/114162/digging-deeper-into-software-artifacts/
- https://blog.1234n6.com/available-artifacts-evidence-of-execution/
- https://github.com/Psmths/windows-forensic-artifacts/blob/main/execution/program-compatibility-assistant.md
- https://blog.1234n6.com/available-artifacts-indicators-of-execution-updated/
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/sygnia_incidentresponse-windows11-windows11-activity-7160666212413157377-MqdZ
- https://mjolnirsecurity.com/the-mjolnir-security-threat-report-unearthing-uncharted-artifacts-in-windows-11/
- https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ArtifactsSsp
- https://docs.velociraptor.app/artifact_references/pages/windows.kapefiles.targets/
- https://www.cybertriage.com/blog/shimcache-and-amcache-forensic-analysis-2025/


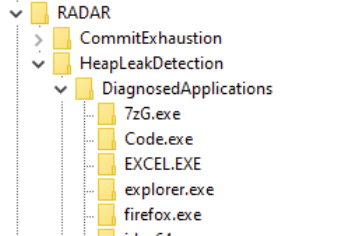 RADAR – An Obscure Execution Artifact
RADAR – An Obscure Execution Artifact Windows Forensics Tools
Windows Forensics Tools LNK File Forensics — Experimental Case Study
LNK File Forensics — Experimental Case Study