Digital forensic investigators encounter significant challenges when dealing with locked computers or encrypted storage systems. Research conducted by Gupta and Nisbet from Auckland University of Technology’s Security \& Forensic Research Group demonstrates a practical technique using RAM cooling methods to preserve memory contents for forensic analysis. Click here to view research paper
The Research Problem
Forensic investigation guidelines typically advise that running computers should be shut down by removing the power supply to preserve hard disk evidence[^3]. However, this standard procedure destroys valuable forensic evidence stored in volatile RAM, including web browsing history, recently run programs, usernames, passwords, and encryption keys.
The research specifically addresses two critical forensic challenges: locked user accounts on running computers and encrypted files that present particular difficulties for investigators attempting to capture forensic images of RAM.
Experimental Setup
Hardware Configuration:
1GB DDR3 non-error correction RAM
Samsung 2.4GHz CPU
Windows 7 operating system[^3]
Data Population Protocol:
The researchers performed six specific actions to populate RAM with forensically relevant data:
Logged into Windows 7 with administrator credentials
Opened text files and copied content to clipboard
Started Apache HTTP web server and MySQL database
Unlocked TrueCrypt file container and opened several files
Executed DOS commands
Launched web browser and logged into Facebook account
Testing Methodology
Baseline Test:
Removing RAM at normal temperature (35°C) and reinserting after 10 minutes resulted in only 0.2% data recovery.
Three Cooling Methods Tested:
| Cooling Method | Temperature | Time Delay(s) | Data Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid Nitrogen | -196°C | 10 min, 1 hr, 2.5 hrs | 99.81%, 98.84%, 93.95% |
| Freezing Spray | -40°C | 10 min | 96.45% |
| Ice Submersion | 10°C | 10 min | 99.71% |
Analysis Process
After cooling, RAM modules were reinserted into the same computer and booted from a USB stick containing DumpIT Linux memory dumping software. The software immediately dumped RAM contents to USB storage for later analysis.
Critical Forensic Discovery
The research successfully recovered 512-bit AES encryption keys used by TrueCrypt in all cooling experiments. This finding demonstrates the ability to decrypt previously inaccessible encrypted files and containers, representing a significant breakthrough for forensic investigators dealing with encrypted evidence.
This research provides empirically proven results through controlled experiments with measurable, reproducible outcomes[^1][^3]. The study demonstrates quantitative data recovery percentages across multiple cooling methods and time delays, validating the practical effectiveness of RAM cooling techniques for forensic investigations.
The successful recovery of TrueCrypt encryption keys specifically validates the forensic value of these techniques in real-world scenarios where encrypted evidence would otherwise remain inaccessible to investigators
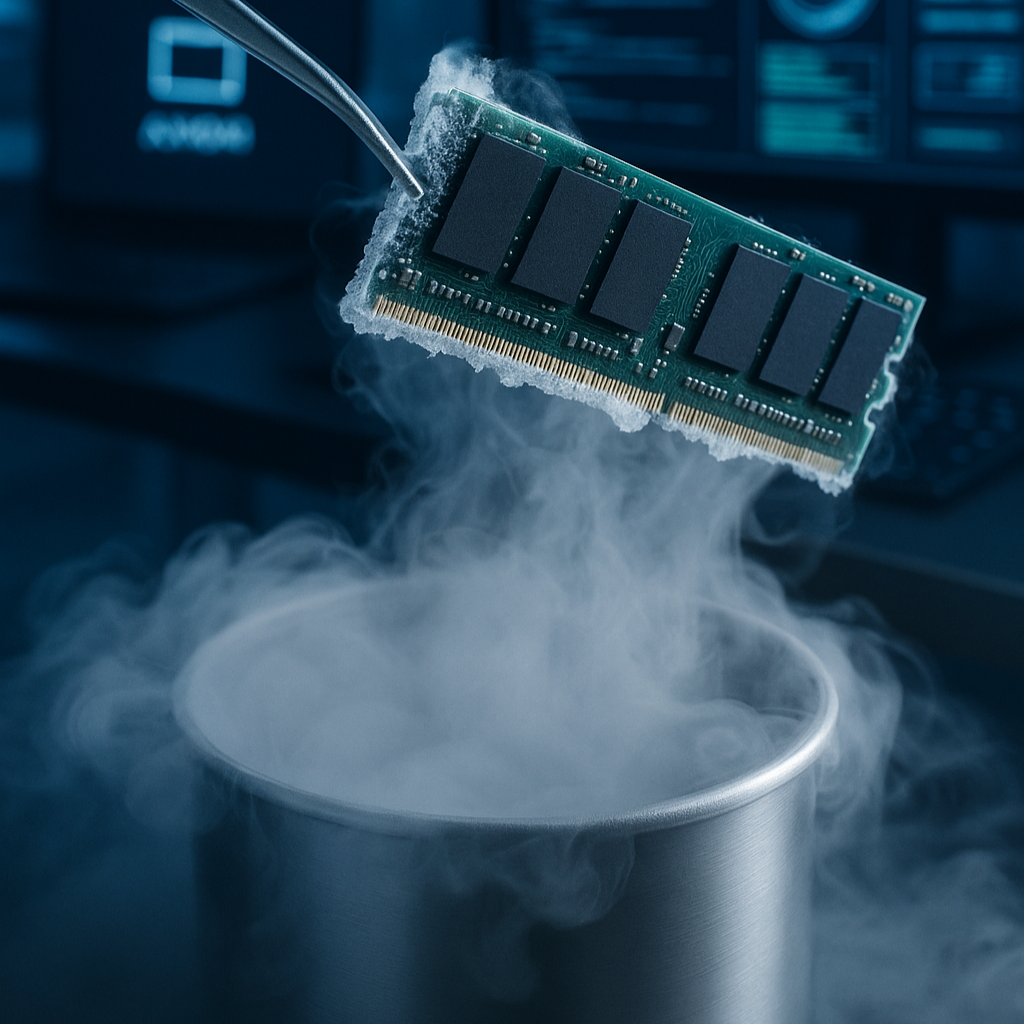
 Acquiring RAM Through Cooling Methods
Acquiring RAM Through Cooling Methods
 Windows Forensics Tools
Windows Forensics Tools LNK File Forensics — Experimental Case Study
LNK File Forensics — Experimental Case Study Windows Artifacts
Windows Artifacts Amcache:The Most Misunderstood Artifact
Amcache:The Most Misunderstood Artifact